Argentina, a vast and diverse country in South America, captivates with its dramatic landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and dynamic society. From the bustling streets of Buenos Aires to the awe-inspiring peaks of the Andes, Argentina offers a tapestry of experiences for visitors and residents alike. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the essence of Argentina, covering its geography, history, culture, economy, and current affairs.
Geography:
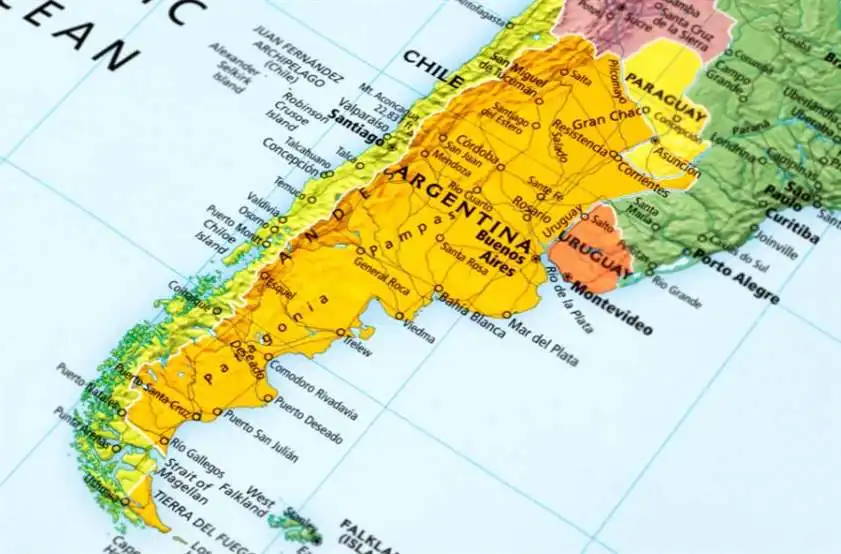
Argentina, the eighth-largest country in the world, occupies the southern part of South America, bordered by Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay to the east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south. Its diverse geography encompasses fertile plains, rugged mountains, vast deserts, and pristine coastline.
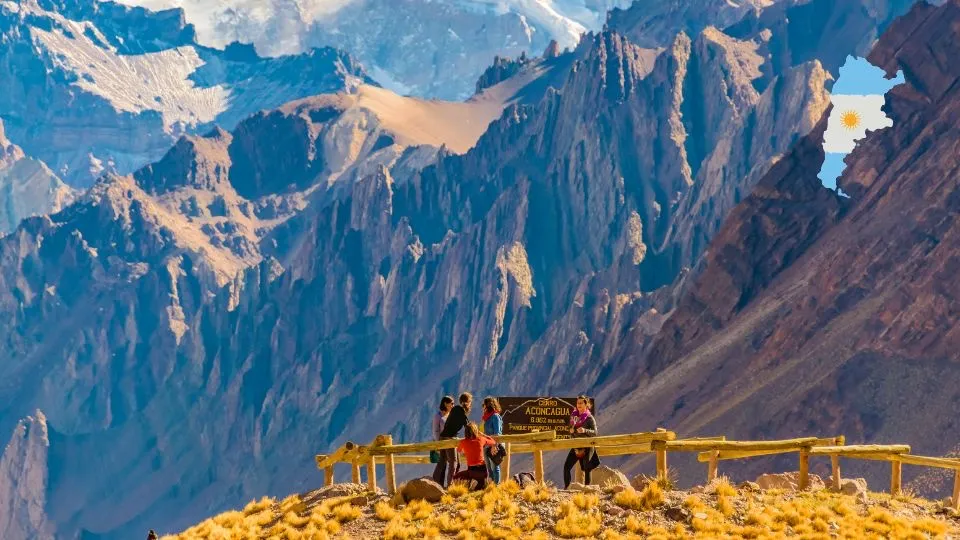
The Andes mountain range forms the natural border between Argentina and Chile, stretching from north to south along the western edge of the country. Mount Aconcagua, the highest peak in the Americas, rises to an elevation of 6,959 meters (22,831 feet) above sea level in the Argentine Andes.
To the east of the Andes, the Pampas region is a vast lowland plain that covers much of central Argentina. The Pampas are known for their fertile soil, which supports extensive agriculture and livestock grazing, as well as their grasslands, wetlands, and estuaries.
In the north, the Gran Chaco region is characterized by its hot and humid climate, dense forests, and rich biodiversity. The Chaco is home to indigenous peoples such as the Toba, Wichi, and Qom, who have adapted to the region’s harsh conditions and maintain their traditional way of life.
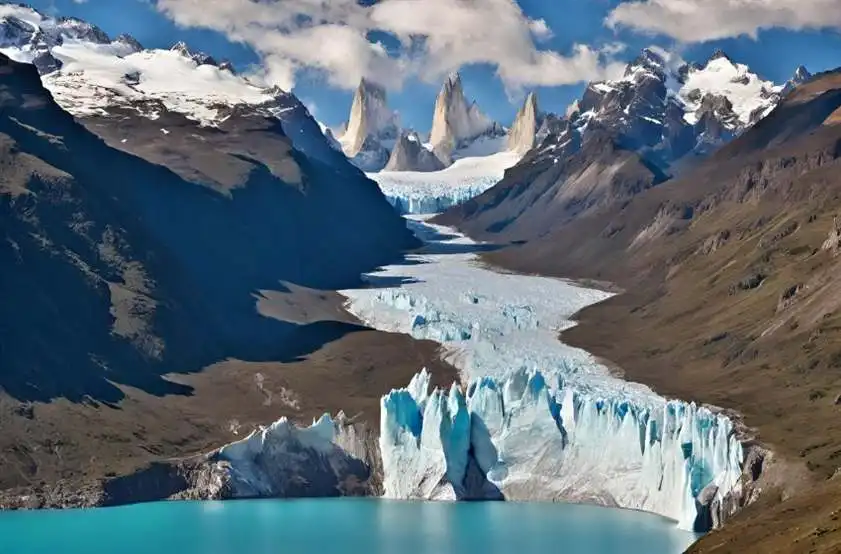
To the south, the Patagonia region is a vast and sparsely populated wilderness of deserts, steppes, and mountains. The region is known for its rugged beauty, pristine wilderness areas, and abundant wildlife, including guanacos, pumas, and Andean condors.
History:
Argentina’s history is a saga of indigenous civilizations, European colonization, and struggles for independence and democracy. Before the arrival of Europeans, the region was inhabited by various indigenous peoples, such as the Mapuche, Guarani, and Quechua, who had established complex societies with rich cultural traditions.
In 1516, Spanish explorer Juan Díaz de Solís became the first European to set foot in present-day Argentina during his search for a passage to the Pacific Ocean. The Spanish began to colonize the region in the 16th century, establishing settlements such as Buenos Aires and Cordoba and bringing Catholicism, the Spanish language, and European customs and laws to the indigenous peoples.
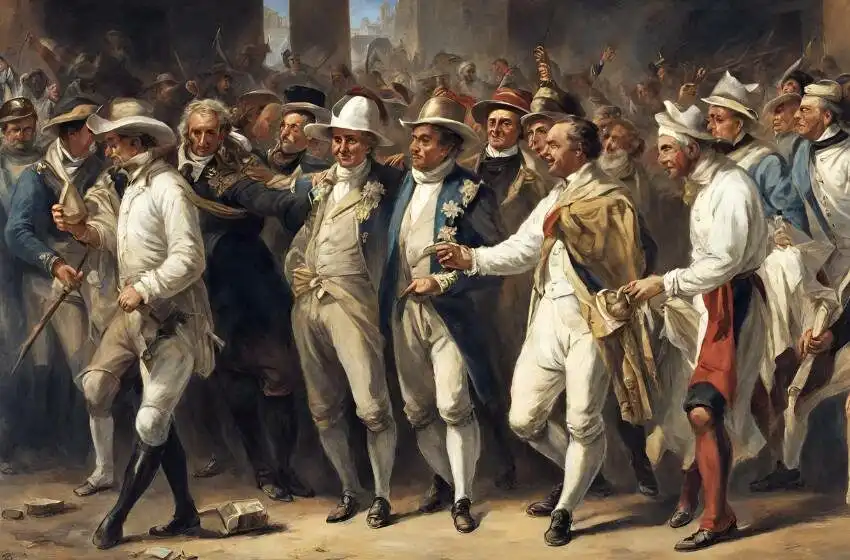
Argentina gained independence from Spain in 1816, following a long and bloody struggle against colonial rule. The country’s first president, José de San Martín, played a key role in the fight for independence, leading military campaigns against Spanish forces and liberating Argentina, Chile, and Peru from Spanish rule.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Argentina experienced waves of immigration from Europe, particularly from Italy, Spain, and Germany, which transformed the country into a melting pot of cultures and peoples. Buenos Aires became a cosmopolitan city with a thriving cultural scene, attracting artists, writers, and intellectuals from around the world.

Culture:
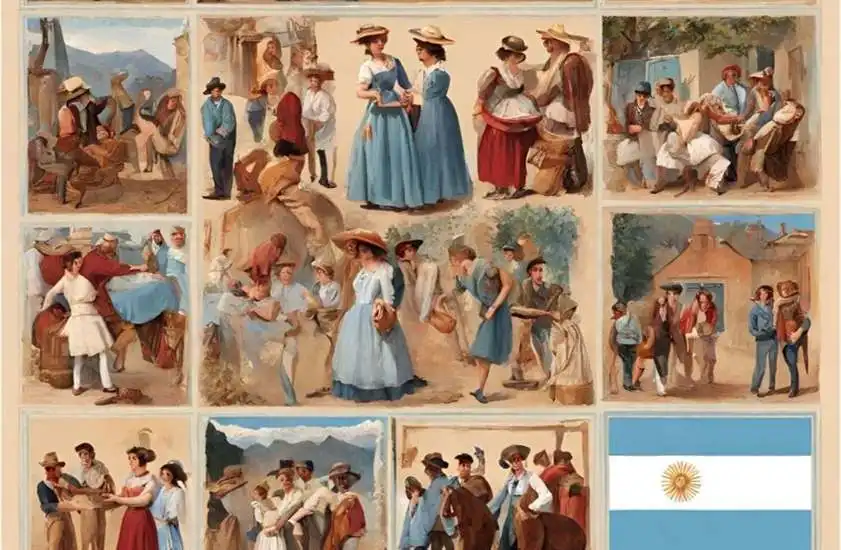
Argentina’s culture is a vibrant blend of indigenous, European, and mestizo influences, reflected in its music, dance, art, literature, and cuisine. From tango to gaucho culture, Argentina’s cultural heritage is celebrated around the world for its passion, creativity, and authenticity.
Music is an integral part of Argentine culture, with genres such as tango, folk, and rock enjoying widespread popularity. Tango, a sensual and dramatic style of music and dance originating in the working-class neighborhoods of Buenos Aires, is synonymous with Argentine identity and has been declared an intangible cultural heritage of humanity by UNESCO.
Dance is also a cherished tradition in Argentina, with styles such as chacarera, zamba, and milonga being performed at festivals, celebrations, and social gatherings throughout the country. Folk dances often incorporate elements of indigenous, African, and European culture, reflecting Argentina’s multicultural heritage.
Argentine cuisine is diverse and flavorful, with dishes such as asado, empanadas, and mate showcasing the country’s culinary traditions. Asado, or barbecue, is a beloved Argentine tradition, with families and friends gathering to grill various cuts of meat over an open flame. Empanadas, stuffed pastries filled with meat, cheese, or vegetables, are enjoyed as a snack or appetizer, while mate, a caffeine-rich tea made from the leaves of the yerba mate plant, is a cultural symbol of friendship and hospitality.

Economy:
Argentina has a mixed economy with a diverse range of industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, services, and tourism. The country is one of the largest economies in Latin America and a member of the G20, with a high standard of living, advanced infrastructure, and a skilled workforce.
Agriculture is a significant contributor to Argentina’s economy, employing millions of people and generating export revenue. The country is a leading producer of grains such as soybeans, corn, and wheat, as well as livestock such as cattle, sheep, and poultry. The fertile pampas region is ideal for agriculture, with its rich soil and temperate climate supporting high yields of crops and livestock.
Manufacturing is also an important sector of Argentina’s economy, with industries such as automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals playing key roles. The country is a major producer of automobiles, with multinational corporations such as Ford, General Motors, and Toyota operating assembly plants in Argentina and exporting vehicles to markets around the world.
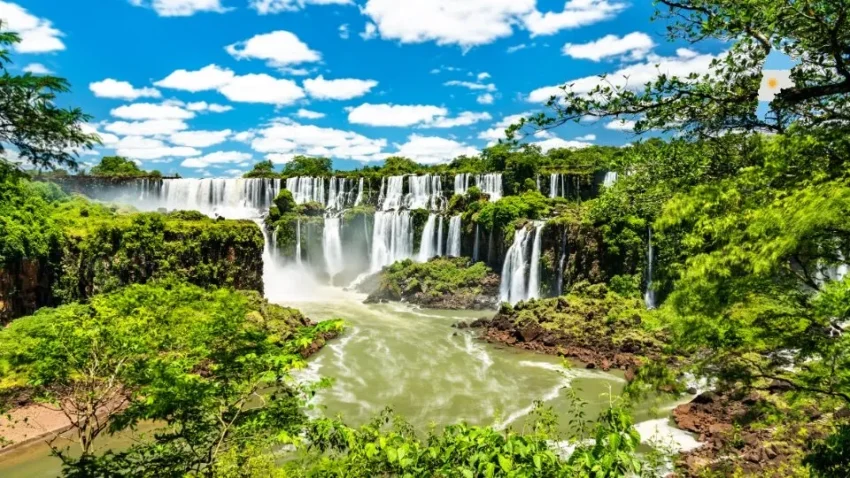
Services, including finance, telecommunications, and tourism, are another significant part of Argentina’s economy, providing employment opportunities and contributing to GDP. Tourism is a major source of revenue for Argentina, with millions of visitors flocking to the country each year to experience its rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning landscapes. Popular destinations such as Buenos Aires, Bariloche, and Iguazú Falls attract tourists from around the world, generating billions of dollars in revenue for the Argentine economy.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites

The most striking curiosities that make unique.
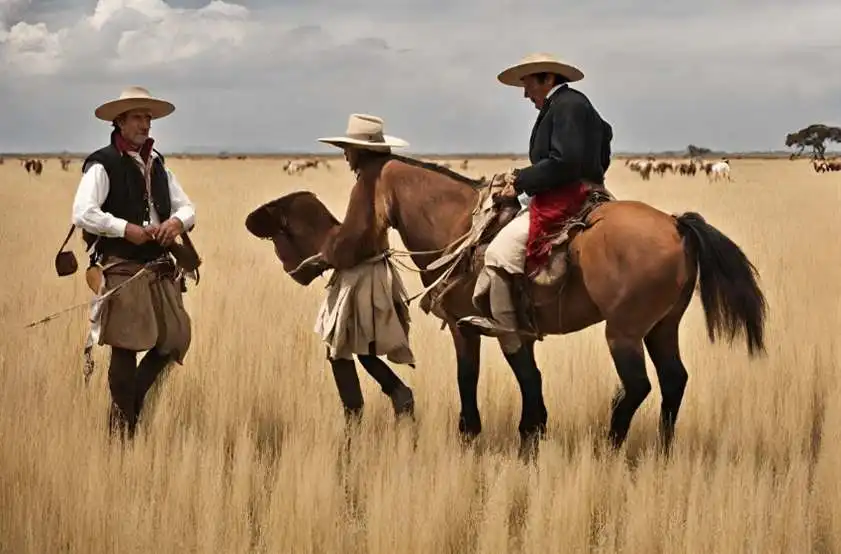

The most touristically renowned places

Conclusion:
Argentina’s story is one of resilience, diversity, and innovation, as the country navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. Its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and dynamic economy make it a unique and fascinating destination in South America. As Argentina continues on its journey of growth and development, it faces numerous challenges and uncertainties, from addressing economic instability and social inequality to promoting environmental sustainability and democratic governance. Despite the complexities and hardships, Argentina’s spirit of resilience, creativity, and optimism shines brightly, inspiring both its citizens and the world at large.



















































Leave a Reply