Bolivia, a landlocked country located in the heart of South America, is a nation of stunning natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and fascinating history. From the snow-capped peaks of the Andes to the vast expanses of the Amazon rainforest and the shimmering salt flats of Salar de Uyuni, Bolivia offers a diverse array of landscapes and experiences for travelers and scholars alike. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the essence of Bolivia, covering its geography, history, culture, economy, and current affairs.
Geography:
Bolivia is bordered by Brazil to the north and east, Paraguay and Argentina to the south, and Chile and Peru to the west. Its geography is characterized by its diverse terrain, which includes the towering Andes Mountains, the sprawling Altiplano plateau, the dense Amazon rainforest, and the arid Chaco region.
The Andes Mountains run through the western part of Bolivia, forming a natural barrier that separates the country from its neighbors. This mountain range is home to some of the highest peaks in the Americas, including Nevado Sajama and Illimani, as well as the world’s highest navigable lake, Lake Titicaca.
The Altiplano plateau, located in the western part of Bolivia, is a high-altitude region known for its stark beauty and extreme climate. It is home to traditional indigenous communities, such as the Aymara and Quechua, who have adapted to the harsh conditions of the Andean highlands.
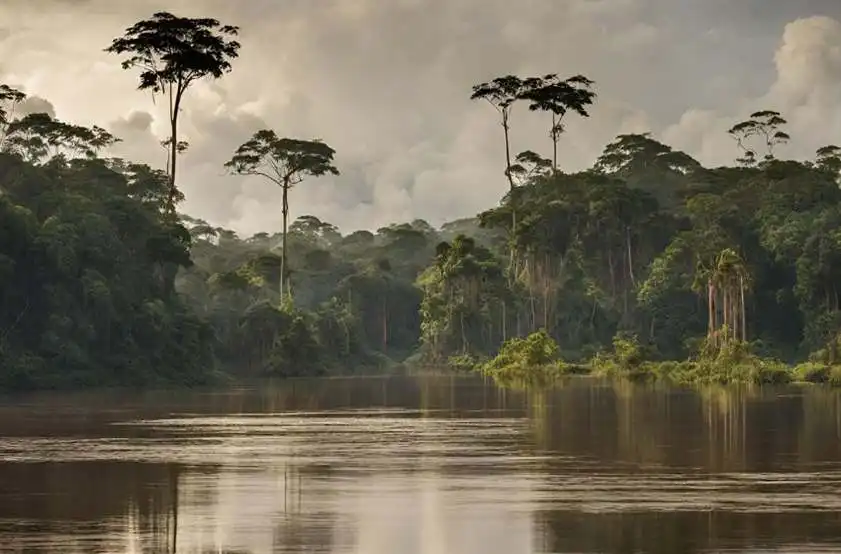
To the east of the Andes lies the Amazon basin, a vast tropical rainforest that covers nearly two-thirds of Bolivia’s territory. This region is home to a rich variety of plant and animal species, as well as indigenous communities that have lived in harmony with their environment for centuries.
The Chaco region, located in the southeast of Bolivia, is a dry, semi-arid plain that extends into Paraguay and Argentina. It is characterized by its scrubland vegetation, sparse population, and unique wildlife, including the iconic jaguar and giant anteater.
History:
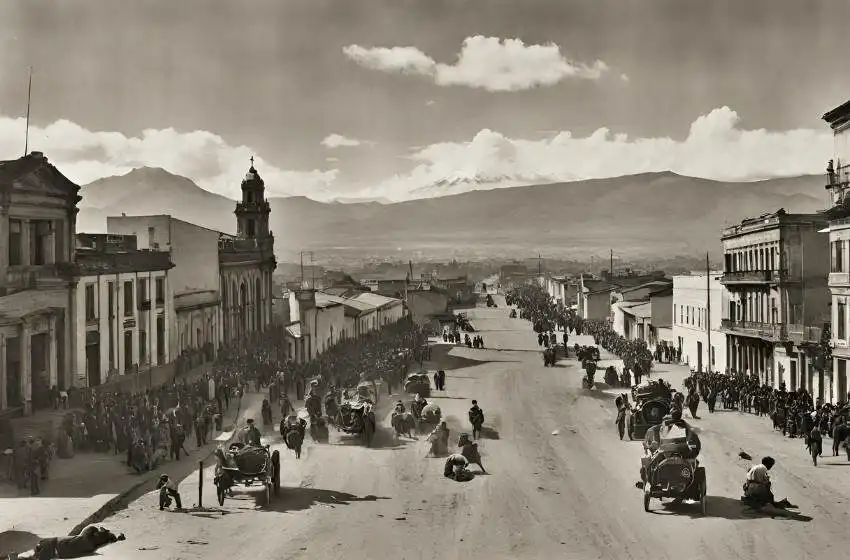
Bolivia’s history is a tapestry woven from the threads of indigenous cultures, Spanish colonization, and struggles for independence and democracy. The territory of present-day Bolivia was originally inhabited by indigenous peoples such as the Aymara, Quechua, and Guarani, who had established sophisticated civilizations and cultural traditions long before the arrival of Europeans.
In 1532, Spanish conquistador Francisco Pizarro arrived in South America and began the conquest of the Inca Empire, which included parts of present-day Bolivia. The Spanish colonization of Bolivia brought about significant changes to the region, including the introduction of Christianity, the Spanish language, and European customs and laws.
The city of Potosí, founded in 1545, became one of the wealthiest and most populous cities in the world due to its rich silver mines. The Spanish extracted vast quantities of silver from Potosí and other mines in Bolivia, leading to enormous wealth for the Spanish crown but also to the exploitation and suffering of indigenous and African laborers.
In 1809, Bolivia declared its independence from Spain, becoming one of the first countries in South America to do so. The struggle for independence was led by figures such as Simón Bolívar, Antonio José de Sucre, and José Manuel de Goyeneche, who fought against Spanish rule and laid the groundwork for the creation of a new nation.
Bolivia’s history since independence has been marked by political instability, social inequality, and struggles for democracy and social justice. The country has experienced numerous coups, revolutions, and periods of authoritarian rule, as well as efforts to address issues such as land reform, indigenous rights, and economic development.

Culture:
Bolivia’s culture is a vibrant mosaic of indigenous, Spanish, African, and mestizo influences, reflected in its music, dance, art, literature, and cuisine. The country’s multicultural heritage is celebrated through colorful festivals, traditional rituals, and a strong sense of national identity.
Music is an integral part of Bolivian culture, with genres such as saya, cueca, and tinku enjoying widespread popularity. Traditional instruments such as the charango, quena, and sikuri are commonly used in folk music, while orchestras and ensembles perform classical and contemporary compositions.
Dance is also a cherished tradition in Bolivia, with styles such as the cueca, morenada, and caporales being performed at festivals, celebrations, and social gatherings throughout the country. Traditional dances often incorporate elements of indigenous, African, and European culture, reflecting Bolivia’s multicultural heritage.
Bolivian cuisine is diverse and flavorful, with dishes such as salteñas, pique macho, and saice showcasing the country’s culinary traditions. Staples such as potatoes, corn, beans, and rice are commonly used in Bolivian cooking, while meats, seafood, and tropical fruits add variety and depth to the cuisine.

Economy:
Bolivia has a mixed economy with a diverse range of industries, including agriculture, mining, manufacturing, services, and tourism. The country is rich in natural resources, including minerals such as silver, tin, and lithium, as well as agricultural products such as quinoa, soybeans, and coffee.
Mining is a cornerstone of Bolivia’s economy, with the country being one of the world’s largest producers of silver and tin. The mining industry has attracted significant foreign investment and has played a crucial role in driving economic growth and development.
Agriculture is also an important sector of Bolivia’s economy, employing a large portion of the population and generating export revenue. The country’s diverse climate and terrain make it well-suited for a wide variety of crops, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and coca.
Manufacturing has emerged as a key driver of economic growth in Bolivia, with industries such as textiles, food processing, and electronics playing important roles. The country’s strategic location, access to international markets, and favorable trade agreements have attracted foreign investment and facilitated economic development.
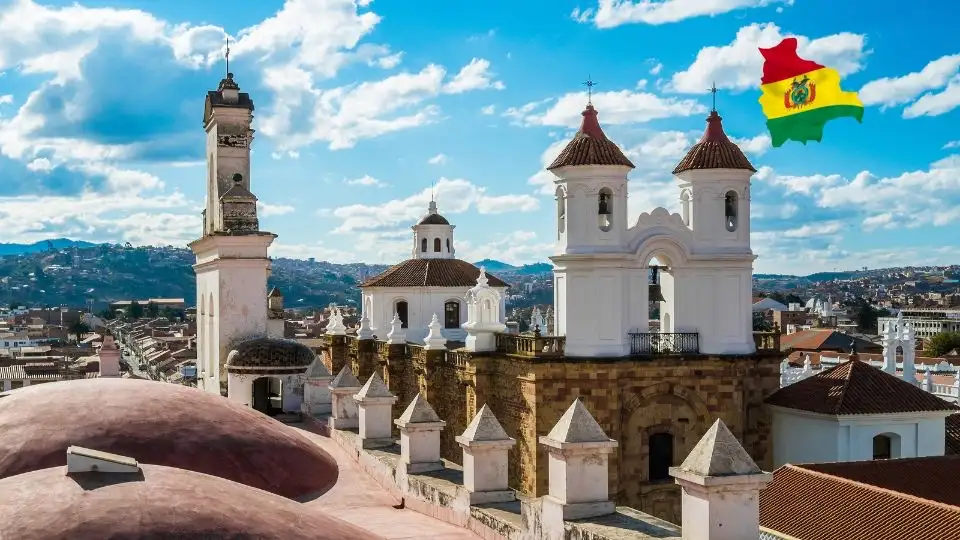
UNESCO World Heritage Sites

The most striking curiosities that make unique:
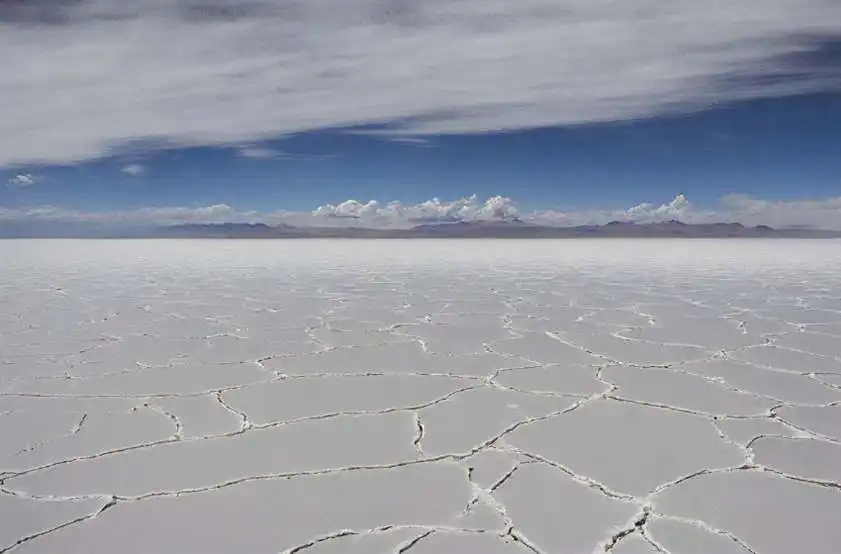

The most touristically renowned places:
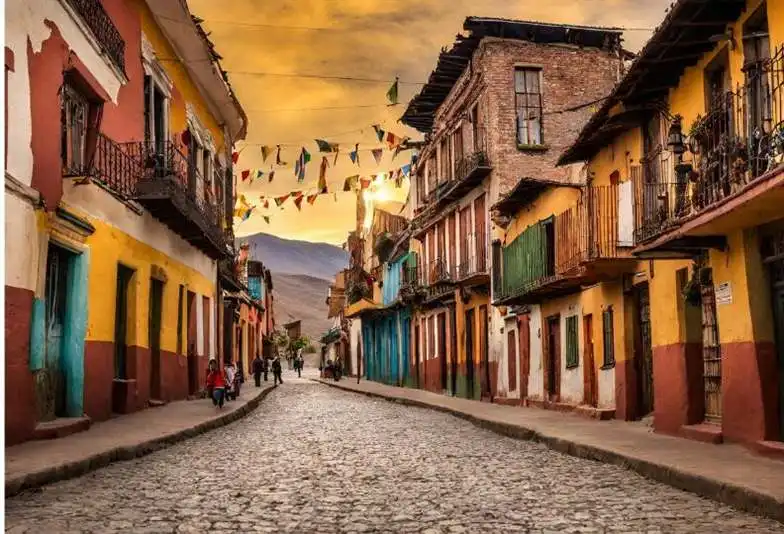

Conclusion:
Bolivia’s story is one of resilience, diversity, and transformation, as the country navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. Its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and enterprising people make it a dynamic and captivating place to explore. As Bolivia continues on its journey of growth and development, it faces numerous challenges and uncertainties, from addressing social inequality and environmental sustainability to promoting economic prosperity and democratic governance. Despite the complexities and hardships, Bolivia’s spirit of resilience, creativity, and optimism shines brightly, inspiring both its citizens and the world at large.
















































Leave a Reply