Cuba, a captivating island nation in the Caribbean, is a land of contradictions, complexities, and resilience. From its revolutionary history to its vibrant culture and stunning landscapes, Cuba has captured the imagination of travelers and scholars alike. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the essence of Cuba, covering its geography, history, culture, economy, and current affairs.
Geography:
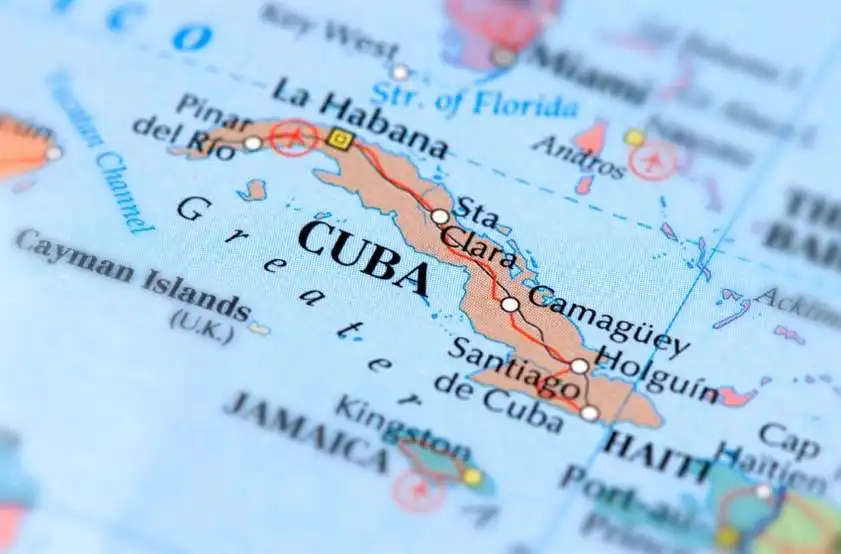
Cuba is located in the northern Caribbean Sea, south of the United States and east of Mexico. It is the largest island in the Caribbean, stretching over 1,200 kilometers (746 miles) from west to east. The island is known for its diverse geography, which includes rolling hills, fertile plains, dense forests, and pristine coastline.
The Sierra Maestra mountain range runs along the southeastern coast of Cuba, with the Pico Turquino peak reaching an elevation of 1,974 meters (6,476 feet) above sea level, making it the highest point in Cuba. The mountains are covered in lush vegetation and are home to a variety of plant and animal species, including the Cuban trogon, the national bird of Cuba.
To the west of the Sierra Maestra, the island is characterized by its fertile plains and valleys, where agriculture is the main economic activity. The Valle de Viñales, located in the western province of Pinar del Río, is famous for its dramatic limestone formations called mogotes and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
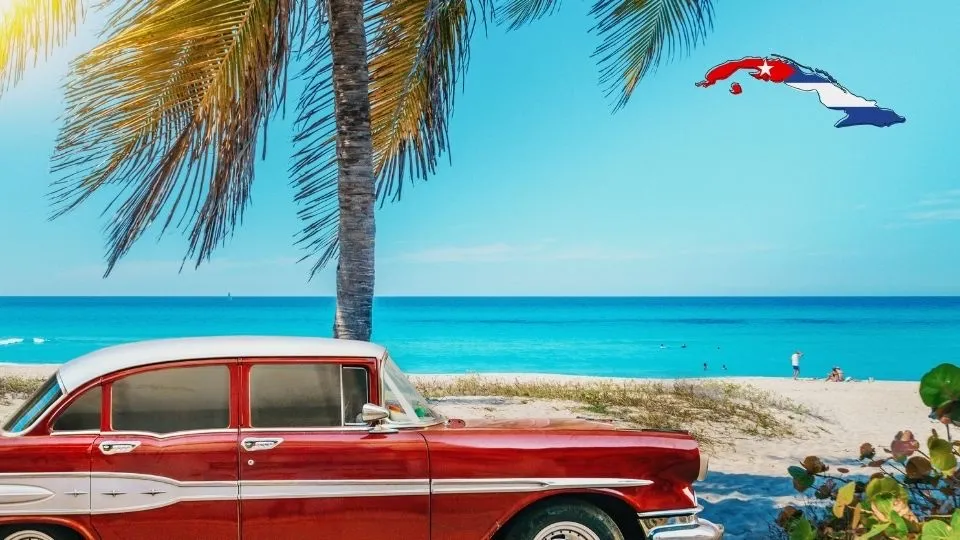
Cuba’s coastline is dotted with sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, and coral reefs, making it a popular destination for beachgoers, divers, and snorkelers. Varadero, Cayo Coco, and Guardalavaca are among the country’s most popular beach resorts, attracting millions of tourists each year.
History:
Cuba’s history is a saga of indigenous cultures, European colonization, African slavery, and revolutionary struggle. Before the arrival of Europeans, the island was inhabited by indigenous peoples such as the Taíno, Ciboney, and Guanahatabey, who had established thriving societies with complex social structures and cultural traditions.
In 1492, Spanish explorer Christopher Columbus arrived in Cuba during his first voyage to the Americas, claiming the island for the Spanish crown. The Spanish began to colonize Cuba in the early 16th century, establishing settlements such as Havana, Santiago de Cuba, and Trinidad and bringing Catholicism, the Spanish language, and European customs and laws to the indigenous peoples.
Cuba became a center of the transatlantic slave trade, with millions of Africans forcibly brought to the island to work on sugar plantations and in other industries. The legacy of slavery is evident in Cuba’s culture, music, dance, and cuisine, which blend African, European, and indigenous influences.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Cuba was a battleground for independence from Spanish rule, culminating in the Spanish-American War of 1898. The United States intervened in the conflict, defeating Spanish forces and establishing Cuba as a protectorate under American influence.
In 1959, revolutionary leader Fidel Castro and his guerrilla army overthrew the American-backed dictator Fulgencio Batista and established a socialist government in Cuba. The Cuban Revolution transformed the country’s political, economic, and social landscape, leading to the nationalization of industries, land reforms, and the establishment of a one-party state.

Culture:
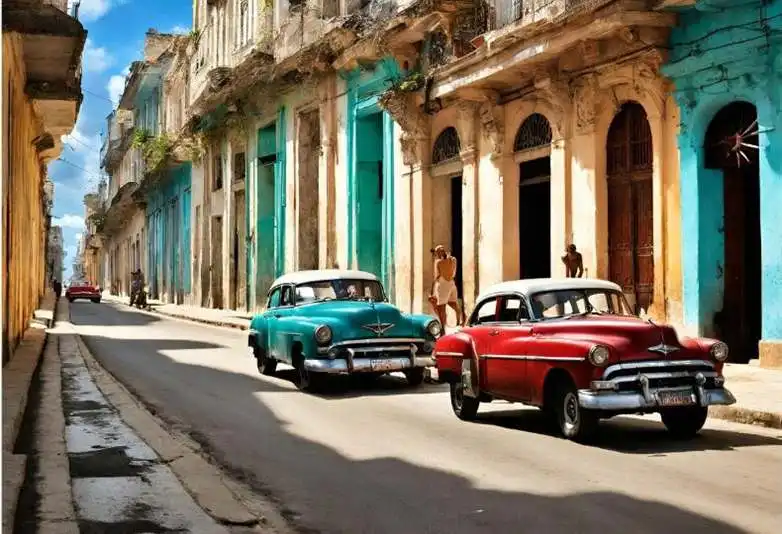
Cuba’s culture is a vibrant fusion of African, European, and indigenous influences, reflected in its music, dance, art, literature, and cuisine. From salsa to rum, Cuba’s cultural heritage is celebrated around the world for its passion, creativity, and authenticity.
Music is an integral part of Cuban culture, with genres such as son, salsa, and mambo enjoying widespread popularity. Son, a traditional style of music and dance originating in eastern Cuba, is characterized by its infectious rhythms, soulful vocals, and intricate instrumentation, including guitars, percussion, and brass instruments.
Dance is also a cherished tradition in Cuba, with styles such as salsa, rumba, and cha-cha-cha being performed at festivals, celebrations, and social gatherings throughout the country. Rumba, in particular, is a dynamic and expressive form of dance that originated in the Afro-Cuban communities of Havana and Matanzas, incorporating elements of African, Spanish, and indigenous culture.
Cuban cuisine is diverse and flavorful, with dishes such as arroz con pollo, ropa vieja, and lechón showcasing the country’s culinary traditions. Staples such as rice, beans, and plantains are commonly used in Cuban cooking, while spices, herbs, and tropical fruits add depth and complexity to the cuisine. Rum, made from sugarcane, is the national drink of Cuba and is enjoyed in a variety of cocktails such as the mojito, daiquiri, and Cuba libre.

Economy:
Cuba has a centrally planned economy with a heavy reliance on state-owned enterprises, government subsidies, and foreign aid. The country’s economy is dominated by the sugar industry, tourism, and remittances from Cubans living abroad, particularly in the United States.
Agriculture is an important sector of Cuba’s economy, with crops such as sugarcane, tobacco, and citrus fruits being grown for domestic consumption and export. The sugar industry was once the mainstay of the Cuban economy, but it has declined in recent decades due to low prices, inefficiency, and competition from other sugar-producing countries.
Tourism is a major source of revenue for Cuba, with millions of visitors flocking to the island each year to experience its rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning landscapes. Popular destinations such as Havana, Varadero, and Trinidad attract tourists from around the world, generating billions of dollars in revenue for the Cuban economy.
Remittances from Cubans living abroad are another important source of income for the Cuban economy, providing financial support to families and businesses across the island. Many Cubans work in the United States and other countries and send money back to their relatives in Cuba, helping to support household consumption and small-scale entrepreneurship.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites

The most striking curiosities that make unique

The most touristically renowned places

Conclusion:
Cuba’s story is one of resilience, resistance, and revolution, as the country navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. Its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and dynamic society make it a unique and fascinating destination in the Caribbean. As Cuba continues on its journey of growth and development, it faces numerous challenges and uncertainties, from addressing economic stagnation and political repression to promoting social justice and environmental sustainability. Despite the complexities and hardships, Cuba’s spirit of resilience, creativity, and optimism shines brightly, inspiring both its citizens and the world at large.


















































Leave a Reply