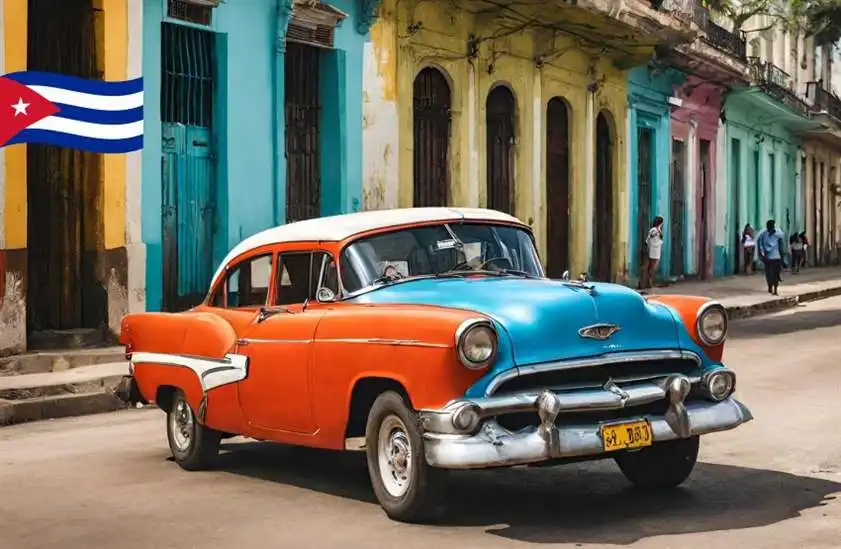
Culture of Cuba, Cuba, the largest island in the Caribbean, is a nation with a culture as captivating and diverse as its history and geography. Over the centuries, this island has been influenced by indigenous peoples, Spanish colonization, African heritage, and even global politics. The result is a vibrant tapestry of traditions, music, dance, art, and a people marked by their resilience and a zest for life. In this 1000-word exploration, we’ll delve into the rich and complex world of Cuban culture.
Historical Roots:
Cuban culture is deeply rooted in its historical past, which includes a series of influences that have shaped its unique identity. Before the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1492, Cuba was inhabited by indigenous peoples, such as the Taíno and Guanahatabey. The Spanish colonization of the island in the early 16th century introduced Catholicism, the Spanish language, and European customs, which continue to play significant roles in Cuban life.
The island’s strategic location made it a valuable possession for Spain, and Havana became a key port for trade. As a result, Cuba saw the arrival of enslaved Africans, whose cultural contributions would profoundly influence the nation’s identity, particularly in music, dance, and religion.
Cuba’s long and tumultuous relationship with the United States, which included the Spanish-American War and the subsequent U.S. occupation, also left a mark on the country’s culture. The Cuban Revolution of 1959, led by Fidel Castro, brought about significant political, economic, and cultural changes that continue to shape the nation.
Cultural Diversity:
Cuba’s cultural diversity is a reflection of its complex history and geographic variety. The country’s population is a blend of indigenous, European, and African influences, resulting in a mestizo majority with a deep connection to their mixed heritage. The African influence is particularly pronounced in the eastern regions of the island, with descendants of enslaved Africans preserving their cultural practices.
Religion, particularly Santería, plays a significant role in Cuban culture, fusing Catholicism with African spiritual traditions. Santería is a syncretic faith that has become an integral part of the Cuban way of life, influencing not only religious practices but also art, music, and dance.
Music and Dance:
Cuban music and dance are at the heart of the country’s culture, celebrated both nationally and internationally. The rhythms of Cuba have had a profound impact on global music. Genres like son, rumba, mambo, and cha-cha-cha have roots in the fusion of Spanish melodies, African percussion, and indigenous influences.
The son cubano is a quintessential Cuban music genre that gave birth to the salsa and influenced many other Latin American musical styles. The clave rhythm, a foundational element of Cuban music, has left an indelible mark on the global music scene.
Cuban dance, with its sensual and rhythmic movements, is an essential part of the culture. The rumba, in particular, is a captivating and expressive dance form that combines African and Spanish elements. The salsa, a high-energy dance style that evolved from Cuban son, has gained worldwide popularity.
Cuisine:
Cuban cuisine is a delightful blend of Spanish, African, and Caribbean flavours. The nation’s staple ingredients include rice, beans, yucca, plantains, and pork. A traditional Cuban dish is the arroz con frijoles negros (rice and black beans), often served with a side of tostones (fried plantains).
The Cuban sandwich, a delectable combination of roasted pork, ham, Swiss cheese, pickles, and mustard, is a culinary icon that originated in Cuban communities in the United States.
Cuban coffee is known for its rich and robust flavour, and the island’s tropical fruits, such as guava, papaya, and mango, are often used in desserts and beverages.
Art and Craftsmanship:
Cuban art is a testament to the country’s creative spirit and cultural diversity. The island has produced a wealth of renowned visual artists. Wifredo Lam, a Cuban-Chinese artist, is celebrated for his fusion of African, Caribbean, and European influences in his paintings.
José Bedia, another influential Cuban artist, explores themes of spirituality, identity, and the African diaspora through his art. The San Alejandro Academy of Fine Arts in Havana has produced a multitude of talented painters and sculptors.
Cuban craftsmanship includes a wide range of artisanal products, from ceramics and woodwork to textiles and jewellery. These crafts often incorporate elements of the island’s natural beauty and cultural diversity.
Festivals and Traditions:
Cuba hosts a wide array of festivals and traditions that showcase its cultural richness and vitality. The Carnaval de Santiago de Cuba is one of the most famous celebrations, featuring colourful parades, music, dance, and vibrant costumes. The Santiago de Cuba Carnival showcases the African and Spanish influences in Cuban culture.
The Fiesta del Fuego, or Festival of Fire, is held annually in Santiago de Cuba and features a unique blend of Caribbean and African traditions, with vibrant processions, music, and dance.
Languages and Literature:
The official language of Cuba is Spanish, and the country has a rich literary tradition. Authors like José Martí and Alejo Carpentier have made significant contributions to world literature. Their works often explore themes of independence, national identity, and the complex realities of Cuban society.
Natural Beauty and Outdoor Activities:
Cuba’s diverse geography offers numerous opportunities for outdoor activities and exploration. The island boasts beautiful beaches, lush forests, and impressive mountains. The Viñales Valley, with its distinctive limestone formations, is a UNESCO World Heritage site and a popular destination for hiking and rock climbing.
Cuba’s pristine coral reefs and warm waters make it a fantastic location for scuba diving and snorkelling, particularly in areas like the Jardines de la Reina. The country’s lush national parks, such as Topes de Collantes, offer excellent opportunities for hiking and birdwatching.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Cuba has faced various challenges, including economic limitations and political isolation. However, the island is gradually opening up to the world, and there is significant potential for tourism, cultural exchange, and economic growth. The rich cultural heritage, stunning landscapes, and artistic expressions provide unique opportunities for Cuba to thrive in the global arena.
In conclusion, Cuban culture is a rich tapestry of history, resilience, and vibrancy. The fusion of indigenous, European, and African influences has created a society that values its mixed heritage and celebrates it through music, dance, cuisine, and visual arts. Cubans are marked by their resilience, their love for life, and their deep connection to their unique identity and traditions. Despite challenges, Cuban culture remains a testament to the creativity and strength of its people, offering a captivating glimpse into a nation that continues to cherish its heritage and its role in shaping global culture.















































Leave a Reply