The Dominican Republic, occupying the eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, is a nation characterized by its rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning natural beauty. From its colonial heritage to its diverse ecosystems and welcoming people, the Dominican Republic offers a compelling narrative that intertwines indigenous, African, European, and modern influences. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the essence of the Dominican Republic, covering its geography, history, culture, economy, and current affairs.
Geography:
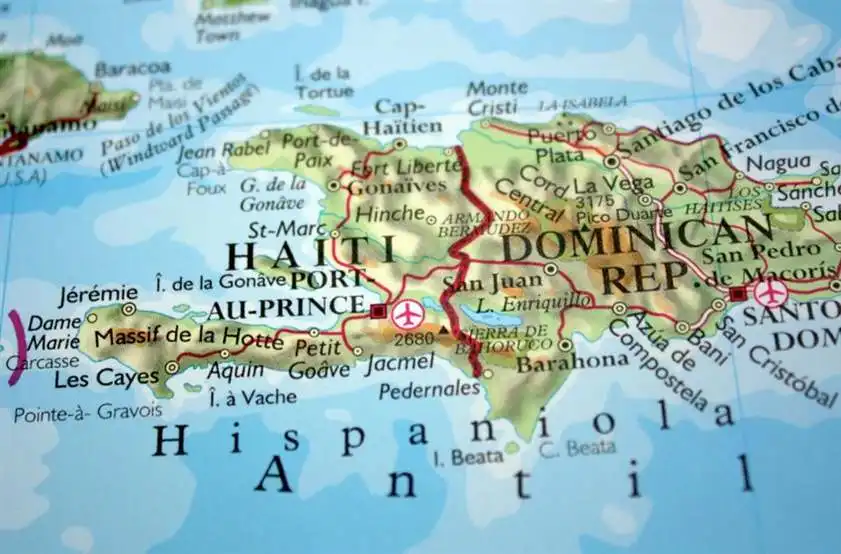
The Dominican Republic shares the island of Hispaniola with Haiti to the west, and it is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and the Caribbean Sea to the south. Its diverse geography includes mountain ranges, fertile valleys, tropical rainforests, arid deserts, and pristine beaches. The country is known for its striking landscapes, with the Cordillera Central mountain range running through its center, including Pico Duarte, the highest peak in the Caribbean.
The Dominican Republic boasts a variety of ecosystems, from the lush rainforests of the interior to the dry forests and savannas of the southwest. The country’s coastline is dotted with picturesque beaches, coral reefs, and mangrove swamps, offering opportunities for tourism, fishing, and marine conservation.
History:
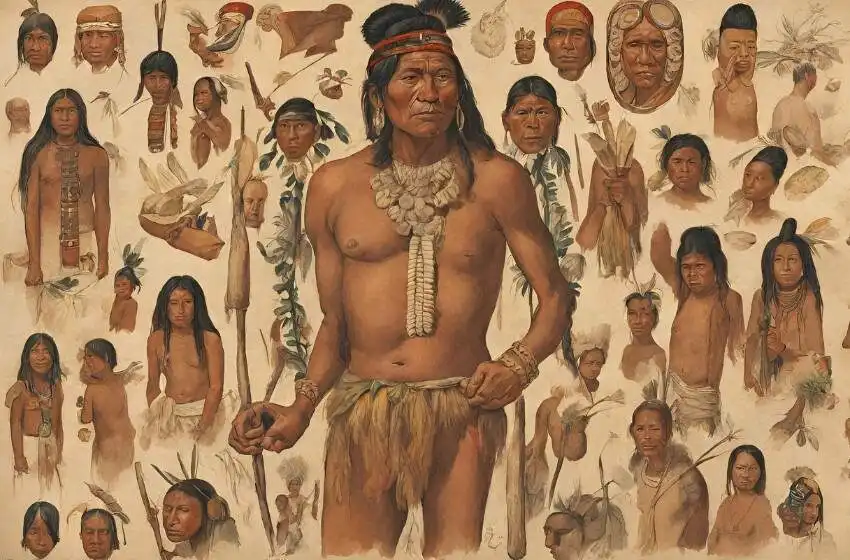
The history of the Dominican Republic is a complex tapestry woven from the threads of indigenous cultures, European colonization, African slavery, and struggles for independence and identity. The island of Hispaniola was inhabited by the Taíno people when Christopher Columbus arrived in 1492, leading to the Spanish colonization of the region.
Santo Domingo, founded in 1498, became the first permanent European settlement in the Americas and served as the capital of Spain’s colonial empire in the New World. The Spanish brought African slaves to the island to work on sugar plantations, leading to a rich cultural fusion of African, European, and indigenous influences.
In 1697, the Treaty of Ryswick divided Hispaniola between Spain and France, with the western third becoming the French colony of Saint-Domingue (now Haiti) and the eastern two-thirds remaining under Spanish control. The colony of Santo Domingo remained loyal to Spain throughout the colonial period, despite attempts by France and other European powers to conquer it.
In 1821, the Dominican Republic declared its independence from Spain, but it was soon annexed by Haiti, leading to decades of political and social turmoil. The Dominican Republic finally achieved independence from Haiti in 1844, establishing itself as a sovereign nation with its own government and constitution.

Culture:
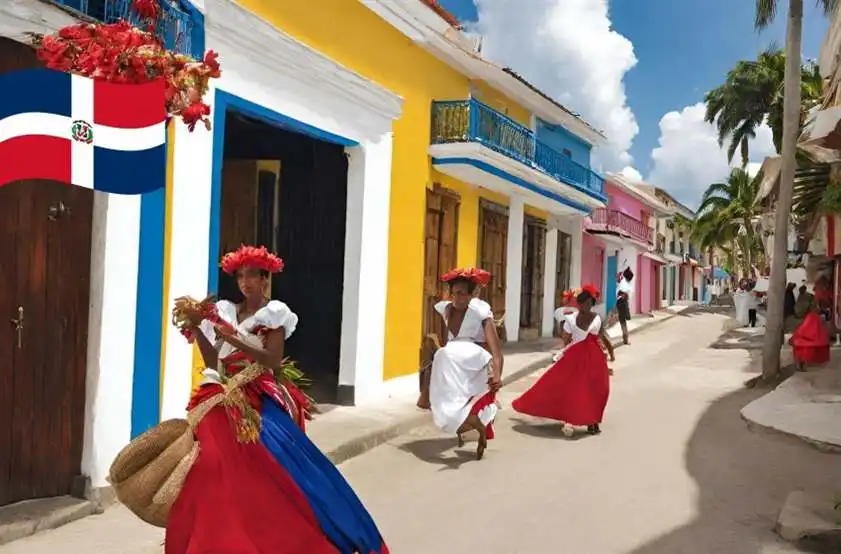
The culture of the Dominican Republic is a vibrant blend of African, European, and indigenous influences, reflected in its music, dance, art, cuisine, and festivals. Merengue and bachata are the country’s most famous musical genres, with their infectious rhythms and melodies capturing the essence of Dominican identity.
Dance is an integral part of Dominican culture, with styles such as merengue, bachata, and salsa being performed at weddings, parties, and festivals across the country. Traditional dances often incorporate elements of African, European, and indigenous culture, reflecting the country’s diverse heritage.
Dominican cuisine is diverse and flavorful, with dishes such as mangu, sancocho, and mofongo showcasing the country’s culinary traditions. Staples such as rice, beans, plantains, and yuca are commonly used in Dominican cooking, while meats, seafood, and tropical fruits add variety and depth to the cuisine.

Economy:
The Dominican Republic has one of the largest economies in the Caribbean, with a diverse range of industries including tourism, agriculture, manufacturing, services, and mining. The country’s strategic location, stable political environment, and open market economy have attracted foreign investment and facilitated economic growth and development.
Tourism is a major driver of the Dominican economy, with millions of visitors flocking to the country each year to enjoy its beautiful beaches, vibrant culture, and historical attractions. The tourism industry generates significant revenue and employment opportunities, supporting businesses such as hotels, restaurants, and tour operators.
Agriculture is also an important sector of the Dominican economy, with crops such as sugar, coffee, cocoa, and tobacco being major exports. The country’s fertile soil, favorable climate, and abundant water resources make it well-suited for agriculture, providing livelihoods for millions of people in rural areas.
Manufacturing has emerged as a key driver of economic growth in the Dominican Republic, with industries such as textiles, apparel, electronics, and pharmaceuticals playing important roles. The country’s proximity to major markets in North America and Europe, as well as its membership in free trade agreements such as CAFTA-DR, have made it an attractive destination for manufacturing investment.
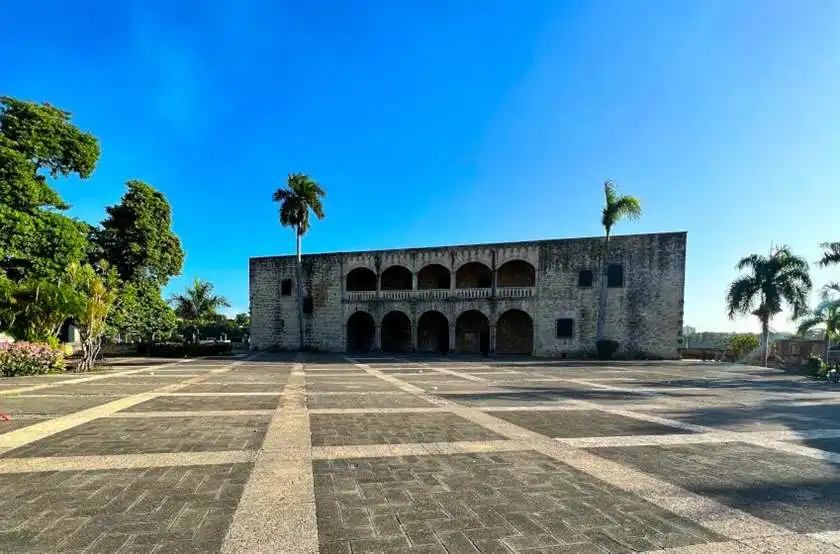
UNESCO World Heritage Sites

The most striking curiosities that make unique:
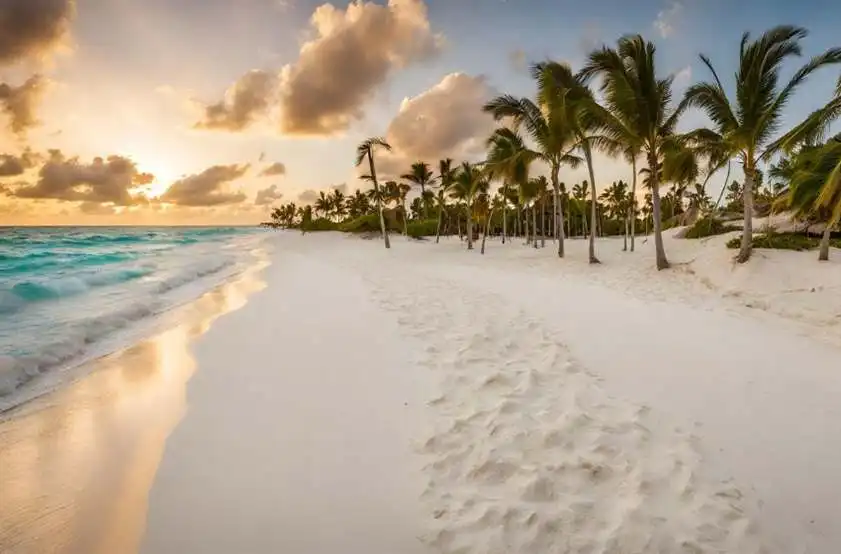

The most touristically renowned places:
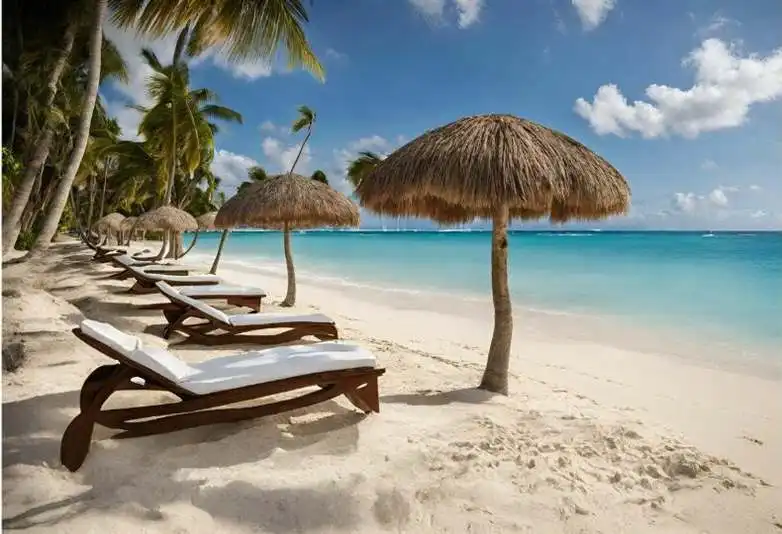

Conclusion:
The Dominican Republic’s story is one of resilience, diversity, and innovation, as the country navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. Its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and dynamic people make it a captivating and inspiring place to explore. As the Dominican Republic continues on its journey of growth and development, it faces numerous challenges and uncertainties, from addressing social inequality and environmental sustainability to promoting economic prosperity and democratic governance. Despite the complexities and hardships, the Dominican Republic’s spirit of resilience, creativity, and optimism shines brightly, inspiring both its citizens and the world at large.
















































Leave a Reply